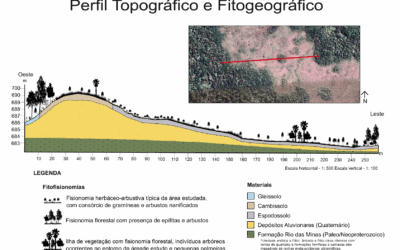
This study investigates the Campo do Veludo, an isolated grassland formation within the Atlantic Forest in southern São Paulo. By integrating soil, topographic, and vegetation data, the research shows that shallow, acidic, and poorly drained Spodosols shape the landscape structure and constrain forest expansion, resulting in a biogeographic enclave of exception. The authors also explore possible connections with muçununga formations, broadening the discussion on landscape diversity in humid tropical regions.
Gustavo Schacht